What Is a Production Line?
A production line, often confused with an assembly line, is a manufacturing process that combines human and machine actions to create products for consumption. Unlike assembly lines, production lines involve a variety of tasks beyond just assembling components, making them more versatile in their functions.
Production lines have evolved through the industrial revolutions, adapting to different manufacturing needs. Today, they are used across various industries, ensuring efficient production with minimal waste.
5 Key Types of Production Lines
Each type of production line serves a specific manufacturing need based on product complexity, customization, and production volume. Here’s a look at the five main types:
1. Mass Production Line

Mass production is the most recognized type of production line. Every product produced is identical in form, size, and functionality. This method ensures consistency across large volumes, making it ideal for products that don’t require customization.
Example: The Ford Model T is a classic example of mass production. Every car produced was identical, allowing for efficient, high-speed manufacturing at a lower cost.
2. Batch Production Line

Batch production allows for the creation of products in groups or batches. While every item within a batch is identical, future batches can vary based on design or other factors.
Example: Limited edition Coca-Cola cans for a holiday season represent batch production. Each can in the holiday batch shares the same design, but it differs from the regular non-holiday batches.
3. Project or Job Production Line

Project or job production lines are flexible, allowing customization for specific customer orders. This type of line is often used for complex, one-time projects where each job differs from the last.
Example: In infrastructure, manufacturing railroad tracks requires customization based on the client’s specifications, making this a project-based production line.
4. Just-In-Time (JIT) Production Line

JIT production creates products only when an order is placed, minimizing waste and reducing inventory costs. It’s a demand-driven system designed for immediate production.
Example: A restaurant kitchen operates as a JIT production line, preparing meals only when orders are placed by diners.
5. Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) Production Line

FMS allows for customization across different product lines. A product moves through various workstations where specific tasks are performed, either by machines or humans, depending on the product’s specifications.
Example: In cosmetics manufacturing, FMS enables the production of compact powders in different shades and sizes, catering to diverse customer preferences.
5 Styles of Production Lines
Production lines can adopt different styles depending on the workflow and product requirements. While some styles are unique to specific types, others can be combined to optimize efficiency.
1. Continuous Flow Production Lines
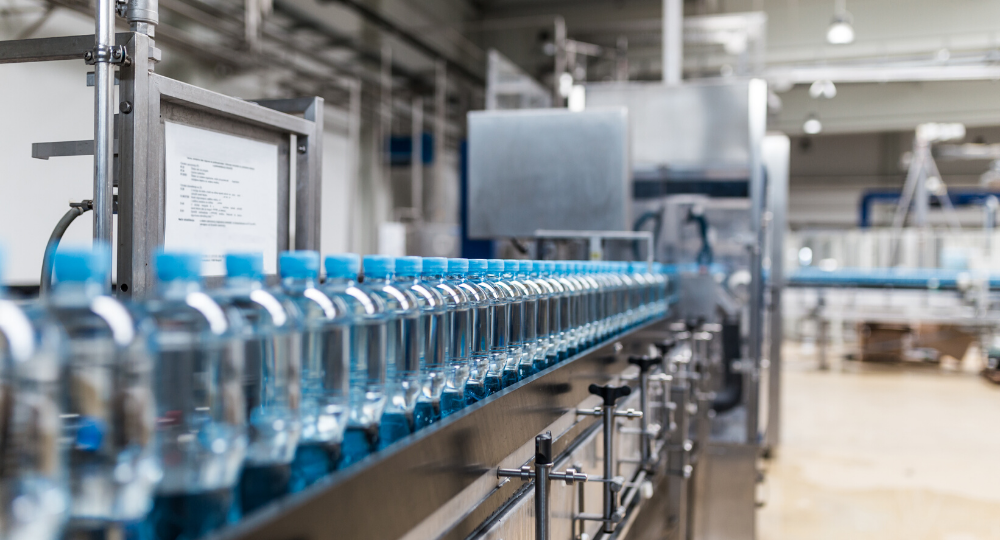

In continuous flow, products are manufactured in a steady, uninterrupted process. There is no variation in the product, making this style ideal for high-volume, uniform items.
Example: Coca-Cola’s production is a continuous flow, ensuring every can produced is identical.
2. Automated Production Lines
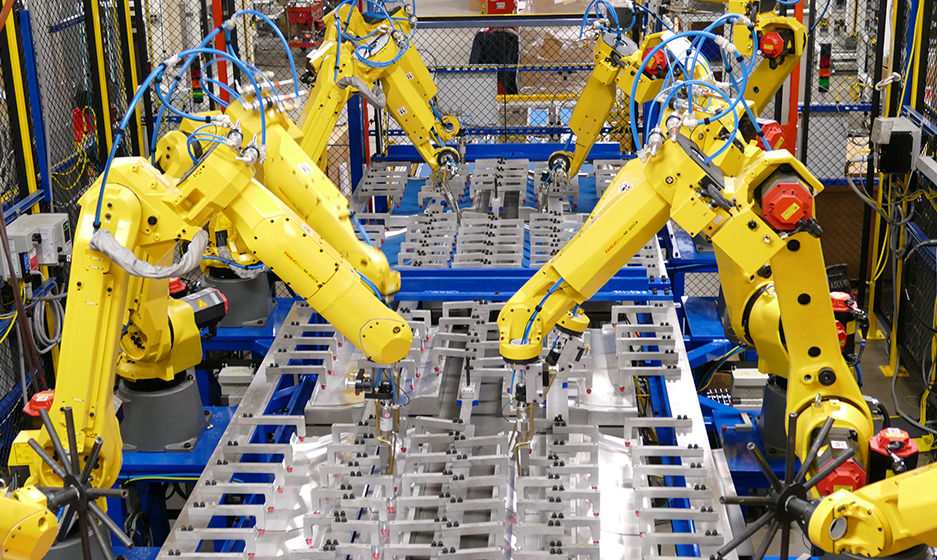
Automated lines rely heavily on machinery to handle repetitive or dangerous tasks. Automation increases precision and speed, making it essential for processes that require consistency.
Example: The electroplating of electronics components is commonly handled by automated production lines.
3. Lean Production Lines

Lean production focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. This style is characterized by methodical frameworks, such as Six Sigma, to improve efficiency and reduce unnecessary steps.
Example: Toyota’s Production System (TPS) is a well-known lean production model that revolutionized post-war Japanese manufacturing.
4. Discrete Production Lines
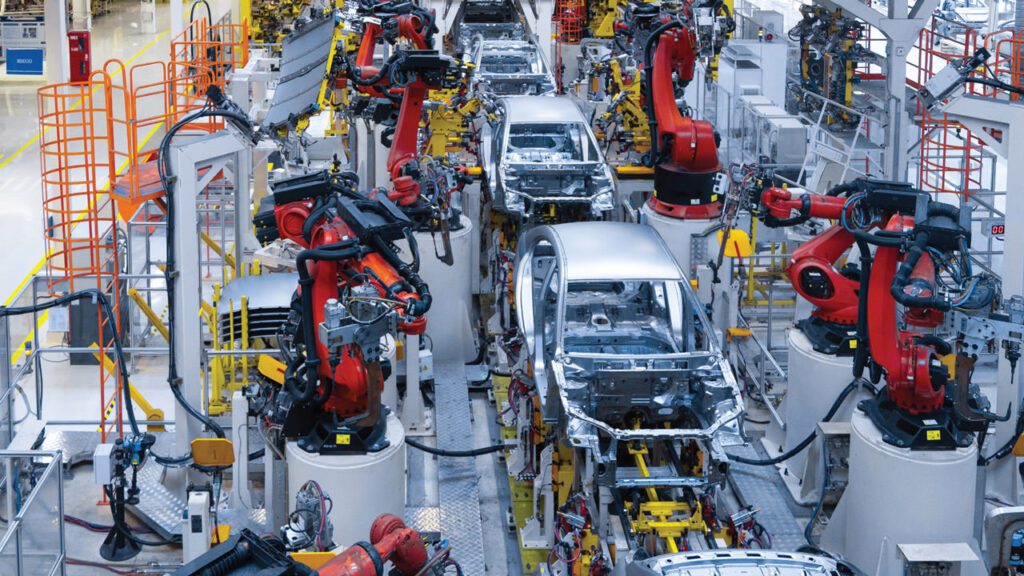

Discrete production lines allow for greater flexibility by producing different items based on current job orders. It contrasts with mass production by offering more customization.
Example: A toy manufacturer that creates a variety of toys for different age groups exemplifies discrete production.
5. Intermittent Production Lines
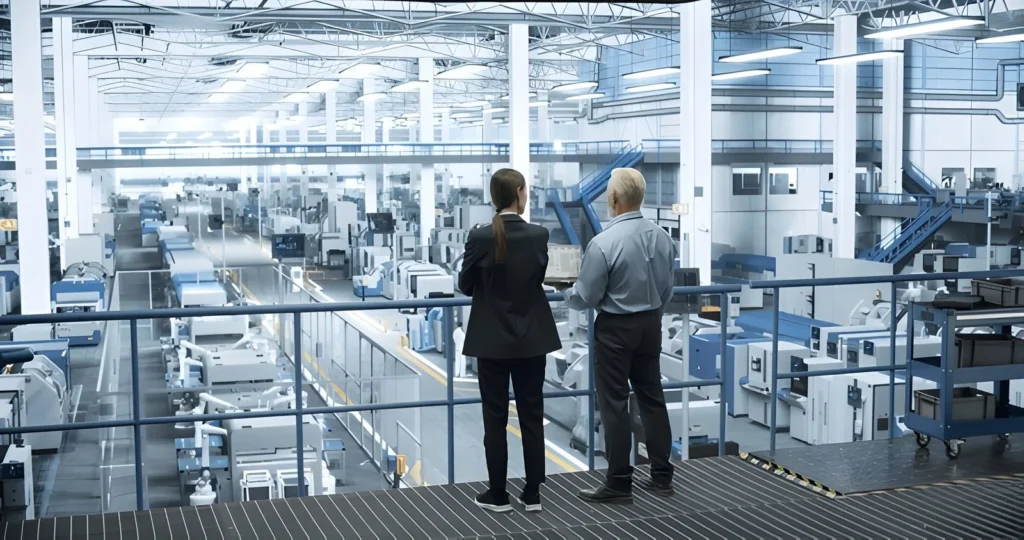

Intermittent production lines make similar products with slight variations. This style is used when products share a common foundation but require minor modifications.
Example: A furniture manufacturer producing a standard design with customizable finishes or colors operates with an intermittent production line.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Production Line
Selecting the correct production line type and style is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency. Companies must evaluate factors such as product demand, customization, and production speed to determine which type and style best suits their needs.
For example, industries producing large volumes of identical items may benefit from a mass production line with a continuous flow style, while companies requiring flexible production might opt for a flexible manufacturing system with discrete production capabilities.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between production line types and styles is essential for optimizing manufacturing processes. From mass production to lean systems, each offers unique benefits tailored to specific industries. By selecting the right approach, companies can enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and better meet customer demands.
Whether you’re in automotive manufacturing, cosmetics, or even food production, the right production line strategy can be the key to success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the most efficient production line style?
A: Continuous flow production is one of the most efficient styles for mass-producing identical items without interruptions.
Q: Can automated production lines reduce labor costs?
A: Yes, automated lines can significantly lower labor costs by minimizing the need for human intervention in repetitive or hazardous tasks.
Q: What is the difference between mass production and batch production?
A: Mass production produces identical items in a continuous process, while batch production creates groups of identical items that can differ from future batches.
What is a Production Line?
A production line is a set of sequential processes used in manufacturing to produce goods. It typically involves a combination of human and machine operations to efficiently create products, with each step in the line performing a specific task to assemble or finish the item.
What is an Example of a Manufacturing Line?
An example of a manufacturing line is an automotive assembly line, where cars are built by adding parts step by step, starting from the chassis and moving through to the installation of the engine, windows, and interior.
What Does a Production Line Worker Do?
A production line worker is responsible for performing specific tasks on a production line, such as assembling parts, monitoring machinery, packaging products, or ensuring quality control. Each worker focuses on a particular step to keep the line moving smoothly.
Why Are Production Lines Important?
Production lines are crucial for increasing efficiency, lowering costs, and producing large quantities of goods quickly. They streamline the manufacturing process, reduce human error, and enable companies to meet high demand consistently.
What Does a Line Production Do?
Line production refers to the process of manufacturing products in a sequential manner. Items move from one station to the next, where specific tasks are completed, ensuring consistent quality and high-speed production.
What is a Production Line Team?
A production line team consists of workers and supervisors who manage the various stages of the production process. Each team member has a specific role, whether it’s operating machinery, overseeing quality, or ensuring that the line runs efficiently.
What Are Three Kinds of Production Lines?
The three common types of production lines are:
- Mass Production Line – Producing large volumes of identical products.
- Batch Production Line – Manufacturing products in groups or batches.
- Just-In-Time Production Line – Producing goods only when there is demand.
What is an Example of a Product Line?
An example of a product line is a smartphone company that offers different models under the same brand, such as budget phones, flagship models, and specialized phones like rugged or foldable devices.
How to Start a Production Line?
To start a production line, you must plan the workflow, design the production layout, acquire necessary machinery and materials, hire and train workers, and implement quality control measures to ensure the smooth operation of the line.
What Does a Production Line Leader Do?
A production line leader supervises workers on the production line, ensuring that the process runs efficiently, safely, and according to schedule. They coordinate tasks, address any issues that arise, and make sure that production targets are met.
What is a Production Line Manager?
A production line manager oversees the entire production line, ensuring that operations are efficient, costs are minimized, and quality standards are maintained. They manage personnel, production schedules, and equipment to optimize the workflow.
What is a Production Line Operator?
A production line operator is responsible for running machinery, monitoring equipment, and ensuring that the production process proceeds without interruptions. They may also handle minor repairs and adjustments to keep the line moving.
What is an Example of a Production Line?
An example of a production line is a bakery where bread is made. The production starts with mixing ingredients, moves on to shaping the dough, baking, and finally packaging the bread for distribution.
What Are Production Lines Called?
Production lines are often referred to as assembly lines, manufacturing lines, or production systems, depending on the industry and the type of products being produced.
What is the Function of a Production Line?
The primary function of a production line is to streamline the manufacturing process by organizing tasks into a sequence, allowing for faster and more efficient production of goods with consistent quality.
To read the latest articles please visit the home page of Turk Blogs.





